 Frogs are belongs to zoological class called Amphibia and there are three kind of categories called Salientia, (frogs and toads), caudate (salamanders and newts) and caecilians (worm-like amphibians).
Frogs are belongs to zoological class called Amphibia and there are three kind of categories called Salientia, (frogs and toads), caudate (salamanders and newts) and caecilians (worm-like amphibians).Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Amphibia
Order: Anura
Frogs has ability to live in various types of climates. You can find these amazing animals in anywhere like in water or desert.
Frogs are cold–blooded animals which mean their body temperature is change according to the environment where they live. Do you know frogs don’t want to drink water like other animals live in the world? Because they have special kind of wet skin which has ability to absorb water. Other specialty of these animals is they can breathe using 2 different ways. By using their lungs and also they can breathe through their skin.

How They Eat
Frogs eats any small kind of insects, small fish, and spiders and also worms. All foods get in to mouth swallowed whole because they can’t chew or bite.
The other amazing feature of this animal is they use their long sticky tongue to catch-up their foods. For a frogs its takes just a less than a second to roll out their tongue and catch the insect and roll back in to their mouth.
To catch–up insect which moving so fast, frogs has large round eyes and also they can see wide range of colors and also can see even in the dim lights. They also can see different direction without moving his heads even little.
Life Cycle of a Frog
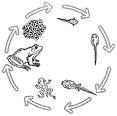 Egg – Female frog laid tiny frog eggs in the water
Egg – Female frog laid tiny frog eggs in the water
Tadpole - (also called the polliwog) Tadpole are the one that coming from the egg. Tadpoles have a little tiny tail and they are in black color and also spend its time swimming in the water
Tadpole with legs – In this time tadpole has legs (and then arms), and a longer body with more distinct head.
Frog let - In this stage, the almost mature frogs breathes with lungs and still have a tail
Adult - The adult frog breathes with lungs and tail is absorbed by their body.
Frogs are very sensitive to changes of the environment. Slight changes in the environment are often detected by frogs well before any other animal. This ability of frogs helps to recover potential problems before it is too late.
Other important of these animals are
They have powerful chemicals in their skins. These chemicals yield a variety of drugs that are useful in medical practices.
Because of the human activities all around the word our amazing frog friends are going to be disappearing. Its time to focus on how important this special amazing animal and try spend some time to save their life.